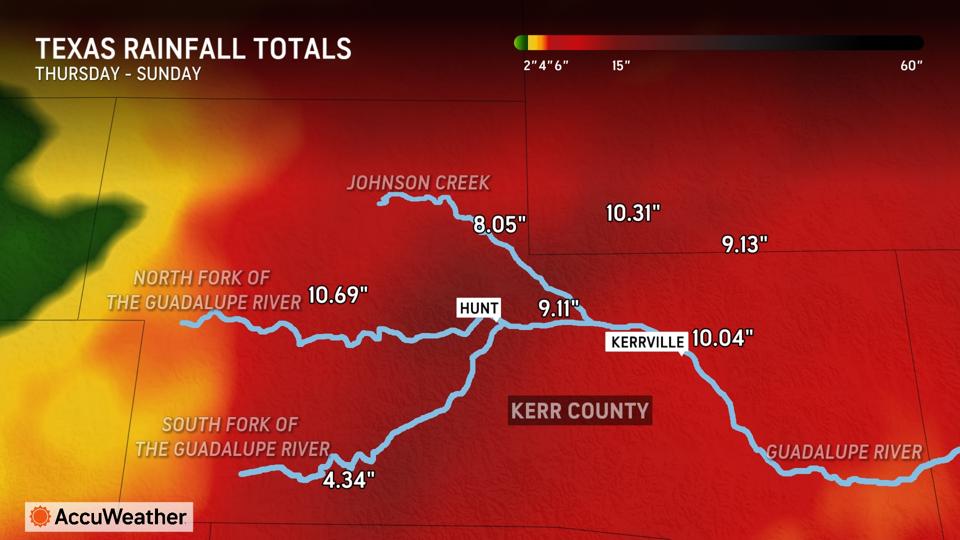
Rainfalls that caused the Texas flood in Kerr County on July 4 2025.
Texas Energy.
Texas is a state where things are big. I recall an oil and gas professional say that Houston was the friendliest large city in the world. Houston has been called the oil capital of the world, for good reason. Costs of doing business, and regulations, are lower in the state than in most other states of the union.
More than that, Texas is blessed with oil and gas, resources that are well correlated with economic position the world over. Oil and gas are cheap and reliable and over the past 100 years have lifted the economic status of populations.
Several years ago, the United States Geological Survey (USGS) announced that the Delaware basin, a part of the Permian basin, contained the largest continuous resources of oil and gas they had ever measured.
It proved to be true as crude oil production ramped up from 2009 until its peak now of almost 7 MMbopd (million barrels of oil per day). A smaller part of this, 2 MMbopd, underlies New Mexico. The Permian is the premier basin for crude oil in the U.S. and one of the best in the world. As a result, in the United States Texas is number 1 producer of crude oil while New Mexico is number 2. The mighty Permian produces about half of total crude oil, and about a third of total U.S. gas.
Oil and gas plays in Texas.
Staying with energy, Texas installed a robust system of wind farms, under the supervision of then-governor Rick Perry, in the period 2000 – 2014. If it were a country, the state was ranked as fifth largest generator of wind power in the world. At 28% of U.S. total, Texas produces more wind energy than any other state in the U.S.
Texas Flood.
This evening, almost 100 people are confirmed dead, and many others still missing, after massive flooding in central Texas. Many of these were camping close to the banks of the Guadalupe River, a beautiful river that people escape from summer’s heat by floating on rafts or inflatable tubes.
Flash flood alley region in central Texas.
Floods are not uncommon in central Texas. And the deadly disaster of July 4, Independence Day, became the latest and perhaps the worst. The flash flood alley extends from the border of Oklahoma north of Dallas to San Antonio in the south, and is reminiscent of the infamous tornado alley, an extended pattern of deadly tornadoes that extends from Kansas south to Oklahoma.
There are reasons for the flood alley in Texas: the hill country is elevated by several hundred feet above sea level, which forces out water from humid clouds blowing in from the Gulf of Mexico. The region consists of hills that induce rainfall and valleys that concentrate the runoff into rivers like the Guadalupe. What makes things worse is that the surface soil layer is thin and washes away rather than soaking up the rain.
The flash flood alley implies lots of previous floodings in the area. To give a wider perspective, Texas has the worst flood heritage in the U.S., if this is defined in terms of discharge per rainfall area. To be clear, this is not the whole of Texas, but the local region of the flash flood alley, which has the worst flooding history, not only for Texas, but also for the entire Unites States.
One meteorologist said that four large-scale flooding events have occurred in the last 50 years in flash flood alley, and one in 1987 caused the death of 10 campers at a nearby Christian camp.
Are The Flood And Energy Connected?
Sadly, there are many emotionally-driven outbursts on social media that claim that emissions from the oil and gas industry cause global warming, and this worsens extreme weather events, such as intense floodings. The first claim is true: the oil and gas industry contributes about 50% of greenhouse gas emissions, and these emissions cause global warming, which has risen by about 1 C degree in the last 40-50 years.
But the second claim is false, and the data confirms this. On a global basis, the four killer weather extreme events (droughts, wildfires, hurricanes, floodings) have not worsened in the past 50 years. Any one of these killer extreme events cannot be blamed on global warming.
Further, the IPCC arm of the United Nations concluded the following about U.S. river floods: “There is limited evidence and low agreement on observed climate change influences for river floods in North America. Based on the peer-reviewed literature and observational records, there is little empirical basis to claim that extreme precipitation has increased in “flash flood alley” (or indeed, most of North America or the world). Similarly, there is little basis for claims that flooding has become more common or severe.”
One curious coincidence: the BBC presented in just the past few weeks a dinosaur documentary that talks about a vast herd of a species called Pachyrhinosaurus that are migrating together. These slow-moving creatures were lumbering along a river valley in Canada when they expired 72 million years ago. Archeologists have uncovered hundreds, probably thousands, of dinosaur bones packed together in death. Apparently, all the creatures were destroyed together by some immense destructive force. And you guessed it—the experts think it was an extreme flash flood.
The flood has been a terrible disaster in Texas. Our thoughts go out to the many families who have lost loved ones, and the remarkable efforts of first-responders who have done their best in rescue efforts. If there’s one lesson to take away, it’s the need for Texas to use its technology might to design better warning systems, such as tornado sirens, for flash floods.