Research by: Jaromír Hořejší (@JaromirHorejsi), Antonis Terefos (@Tera0017)
Key Points
- Check Point Research discovered a multistage campaign targeting Minecraft users via the distribution as a service (DaaS) Stargazers Ghost Network, which operates on GitHub. The malware impersonates, among others, Oringo and Taunahi, which are “Scripts & Macro” tools (a.k.a cheats).
- The first-stage downloader and the second-stage stealer are implemented in Java and require Minecraft to be installed on the host. The third and last stage malware is a .NET stealer with extended capabilities.
- Minecraft malware is written in Java, which is often overlooked by security solutions.
- The malware is developed by a Russian-speaking threat actor and contains several artifacts written in the Russian language.
Introduction
Minecraft is a popular video game with a massive global player base, with over 200 million monthly active players. The game has also sold over 300 million copies, making it one of the best-selling video games ever. Minecraft supports mods (user-created modifications), which enrich the user experience by improving gameplay, fixing bugs, enhancing graphics, and adding new content. It is estimated that more than 1 million players are actively involved in modding Minecraft.
Check Point Research discovered malicious repositories distributing malware via the Stargazers Ghost Network, which operates as a Distribution as a Service (DaaS).
The campaigns resulted in a multi-stage attack chain targeting Minecraft users specifically. The malware was impersonating Oringo and Taunahi, which are “Scripts and macros tools” (a.k.a. cheats). Both the first and second stages are developed in Java and can only be executed if the Minecraft runtime is installed on the host machine.
Stargazers Ghost Network Campaigns
Since March 2025, Check Point Research has been tracking malicious GitHub repositories targeting Minecraft users with an undetected Java downloader. Those repositories supposedly provided mods for Minecraft and appeared legitimate as multiple accounts starred those repositories.
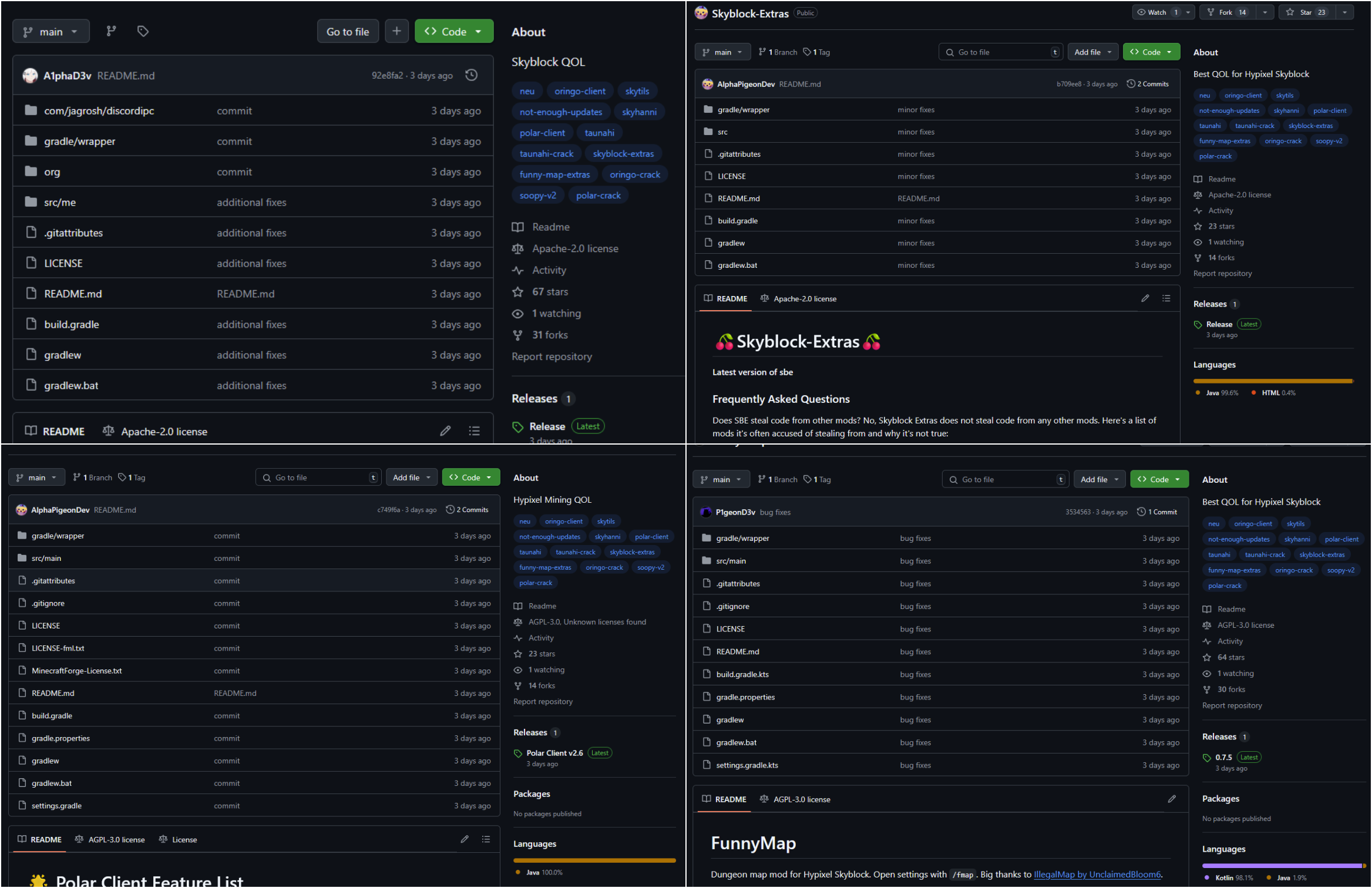
Figure 1: Malicious repositories.
The repositories contained various malicious jar files, and their names usually impersonated various cheat and automation tools. Below are listed the discovered filenames:
FunnyMap-0.7.5.jar Oringo-1.8.9.jar Oringo-Client.1.8.9.jar Polar-1.8.9.jar PolarClient-v2.6.jar SkyblockExtras-1.8.9.jar Taunahi-V3.jar TaunahiPlus-V3.jar
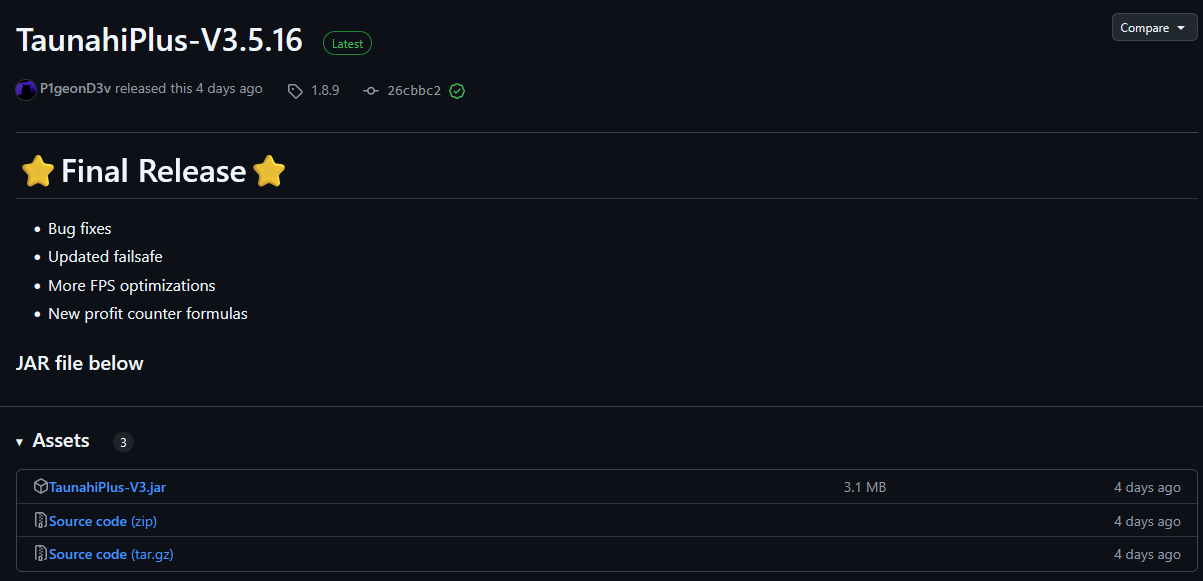
This Java downloader is undetected by all antivirus engines across VirusTotal as it is highly targeted for Minecraft users, and the sandbox engines do not contain the required dependencies, which will let the malware run.
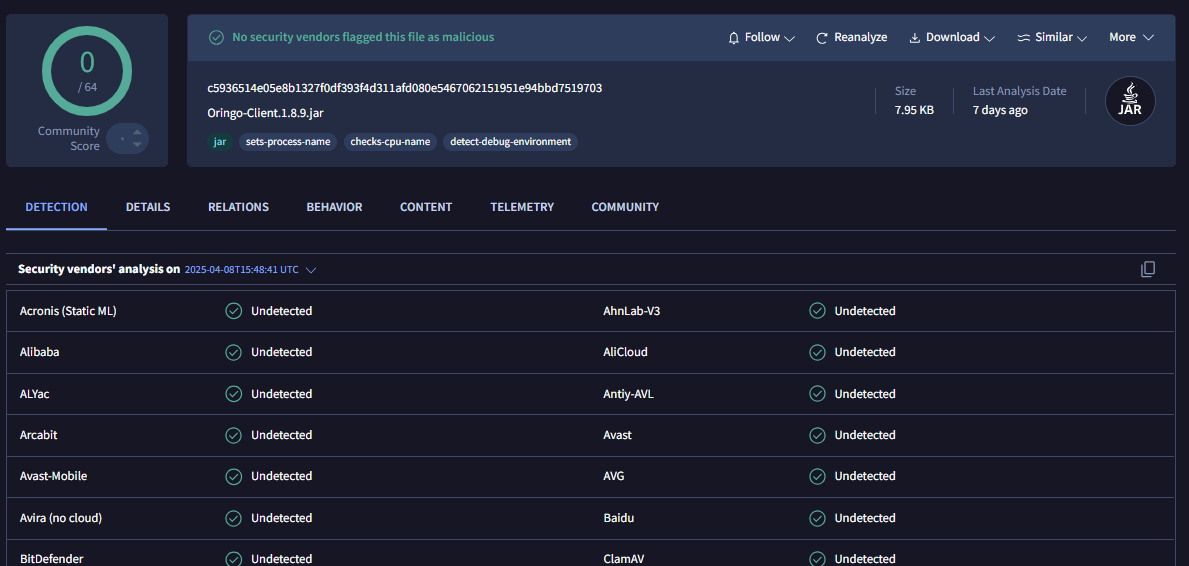
While we have little information about the attacker, one thing is consistent regarding the attacker’s commits, all of them are made in the UTC+3 timezone, and Russian comments found on some malicious files further suggest the probable country of origin.
--> "tree 610486a827b9118c4443601c66524ba8036eb2bb\nparent 32c36b5892d2af4de4bd6c097814e56e672c5b21\nauthor P1geonD3v <[email protected]> 1745610224 +0300\ncommitter GitHub <[email protected]> 1745610224 +0300\n\nREADME.md" --> "tree 4e17fb81ae629b923234147d500c27200ca48e3c\nparent 52f5bf7d2bc69fc89c3dedc85e2f7d7a0255aa9c\nauthor AlphaPigeonDev <[email protected]> 1745613736 +0300\ncommitter GitHub <[email protected]> 1745613736 +0300\n\nREADME.md" --> "tree 9f1b30ca6551bd982e54c4a57e70ab372083fc05\nparent a6e206f07cd91f9a7a2b764808778dbcbae108ec\nauthor A1phaD3v <[email protected]> 1745615260 +0300\ncommitter GitHub <[email protected]> 1745615260 +0300\n\nREADME.md"
Malware overview
The infection chain starts with a hosted JAR archive, which needs to be downloaded and installed manually by the victim as a Minecraft mod (”mod” is a shortcut for “modification”, which is a user-created addition or alteration of the original version. Mods can add new features, enhance game play and customize players’ experience.). When the victim starts the game, the malicious mod downloads the second-stage stealer, which in turn downloads one more .NET stealer. The malware is developed by a Russian-speaking threat actor and contains several artifacts written in the Russian language.
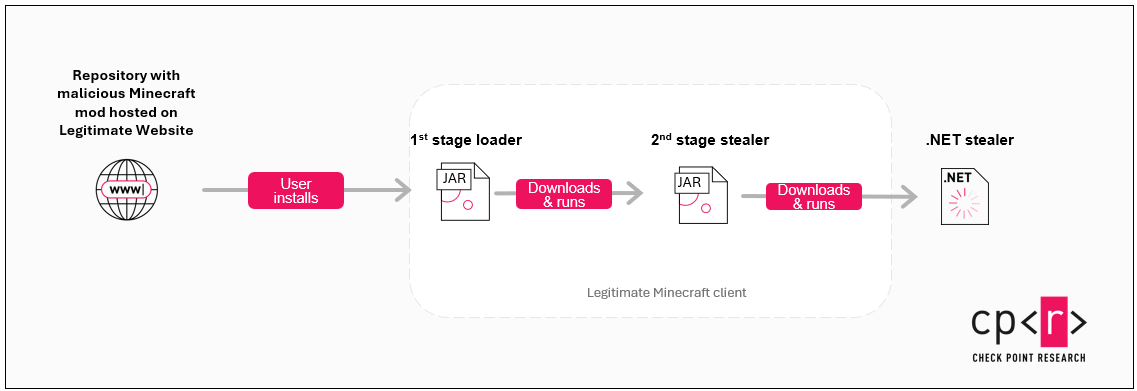
Part I – Static Analysis – 1st Stage Loader
The initial JAR file is designed as a Minecraft Forge mod. It does not have the Main-Class attribute in the manifest, thus, simply running “java -jar ” from the command line does not work. The package names of the first two stages are me.baikal.club, referencing Baikal, the deepest lake in the world, is located in the Asian part of Russia.
In order to develop custom mods, the developer must respect a certain structure and include specific dependencies. The main @Mod class contains a reference to IFMLLoadingPlugin. FML letters stand for Forge Mod Loader.

Loader implements simple anti-VM and anti-analysis techniques. Initially, the loader gets the names of the three following properties (results are equivalent to calling “java -XshowSettings:properties -version”).
- os.name
- java.vm.name
- java.vm.vendor
If any of the above-mentioned settings contain a block-listed keyword (related to various virtual machines), the malware (Minecraft mod) terminates itself. This is the list of block-listed keywords:
vmware virtualbox kvm qemu hyperv xen parallels vbox vpc vboxguest sshd headd
Then, the tasklist utility is called to list all running processes. If any of the block-listed processes are detected, the mod’s execution is terminated. These processes are associated with virtual machines (VBox, Parallels, VMware), protocol analyzers (Wireshark, HTTP Debugger), and programs for listing network connections (TCPView).
This is the list of block-listed processes:
VBoxTray.exe VBoxService.exe prl_cc.exe prl_tools.exe SharedIntApp.exe vmusrvc.exe vmsrvc.exe vmtoolsd.exe Wireshark.exe HTTPDebuggerUI.exe HTTPDebuggerSvc.exe tcpview.exe
After passing the previous checks, the first stage downloads the content of a paste from Pastebin (hxxps://pastebin.com/raw/xCa3vSiP). The base64 encoded content is decoded, and the malware retrieves a link (hxxp://147.45.79.104/download) for the second stage. The downloader loads into memory the Java Stealer with the name MixinLoader-v2.4.jar.
Interestingly, the paste was created by username JoeBidenMama, who created three more pastes:
- Google statistics 3 (plaintext),
hxxp://147.45.79[.]104/cookies - Google statistics 2 (Base64 Encoded),
hxxp://147.45.79[.]104/download - Google statistics (plaintext),
hxxp://147.45.79[.]104 - Google statistics (plaintext),
hxxp://147.45.79[.]104:80
Pastebin’s column “HITS” shows how many times the paste has been seen or downloaded. This can give us a rough estimate of an upper range of how many victims might have been targeted or infected, as the paste is accessed every time the infected plugin is run. Check Point Research kept monitoring this account and discovered further campaigns and paste-URLs being added, and a total number of hits exceeding 1500.
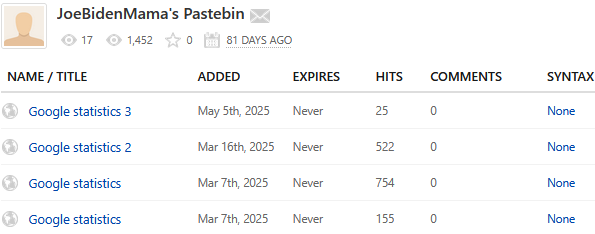
JoeBidenMama with statistics (HITS)Part II – Dynamic Analysis – 1st Stage Loader
To add mods to a Minecraft game, the user must copy the malicious JAR archive into the Minecraft mods folder. After starting the game, the Minecraft process will load all mods from the folder, including the malicious mod, which will download and execute the second stage.
To run the malware dynamically, we decided to install Legacy Launcher. The Minecraft Forge version 1.8.9 is required, as the metadata inside the mcmod.info from the JAR archive reveals that our malicious plugin requires this loader.

Thus, all we need to do is run the Minecraft client and install the proper type and version of mod loader.
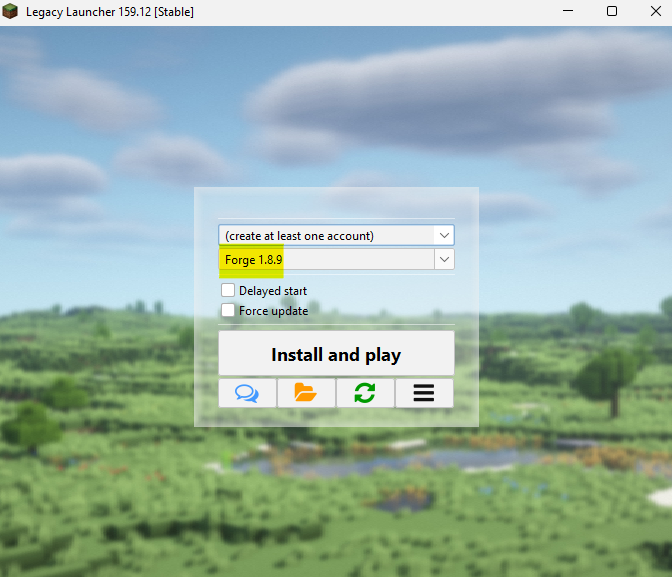
After the installation is complete, we can copy our malicious JAR file into the mods directory (\.tlauncher\legacy\Minecraft\game\mods\) and enter the game, which will activate our malicious mod.
Executing the malicious JAR plugin in a virtual machine, we can notice the execution of tasklist just before the malicious plugin exits due to the detection of the virtual environment. For demonstration purposes, we edit the original JAR mod to execute notepad instead of tasklist. Running such a modified mod executes Notepad, as shown in the animation below.
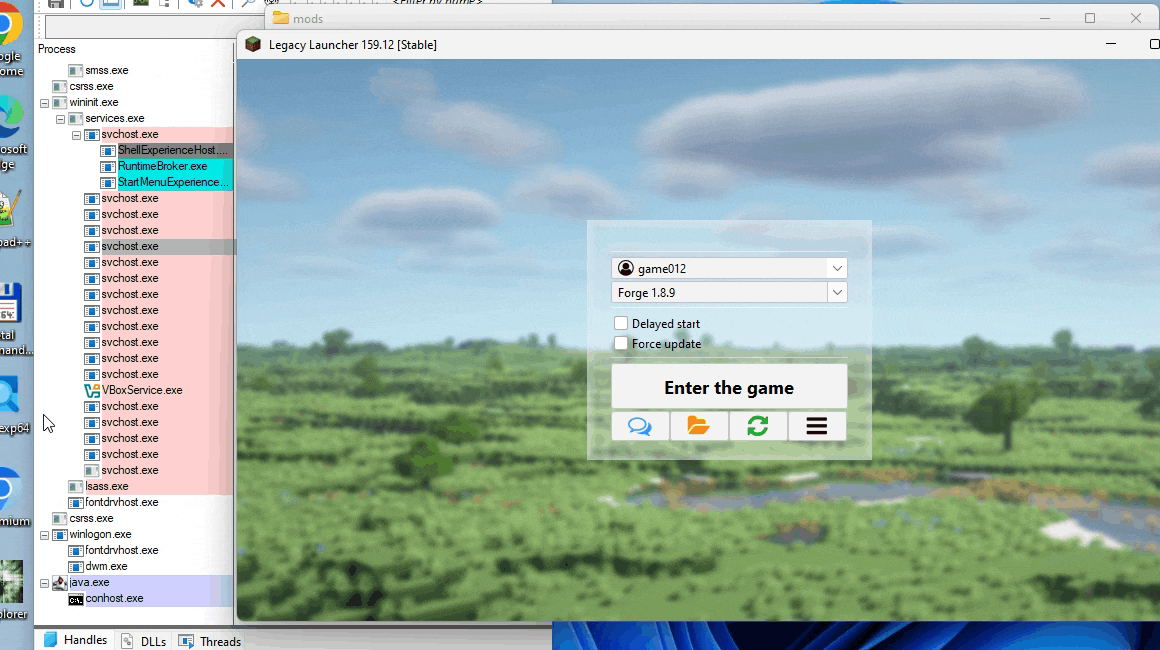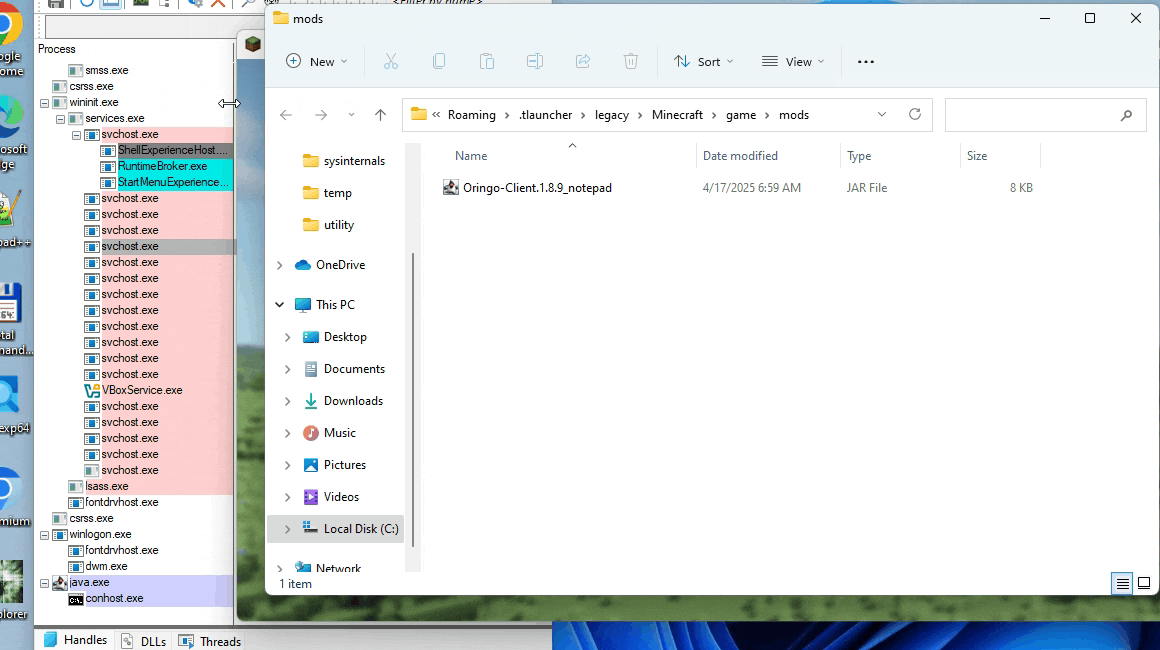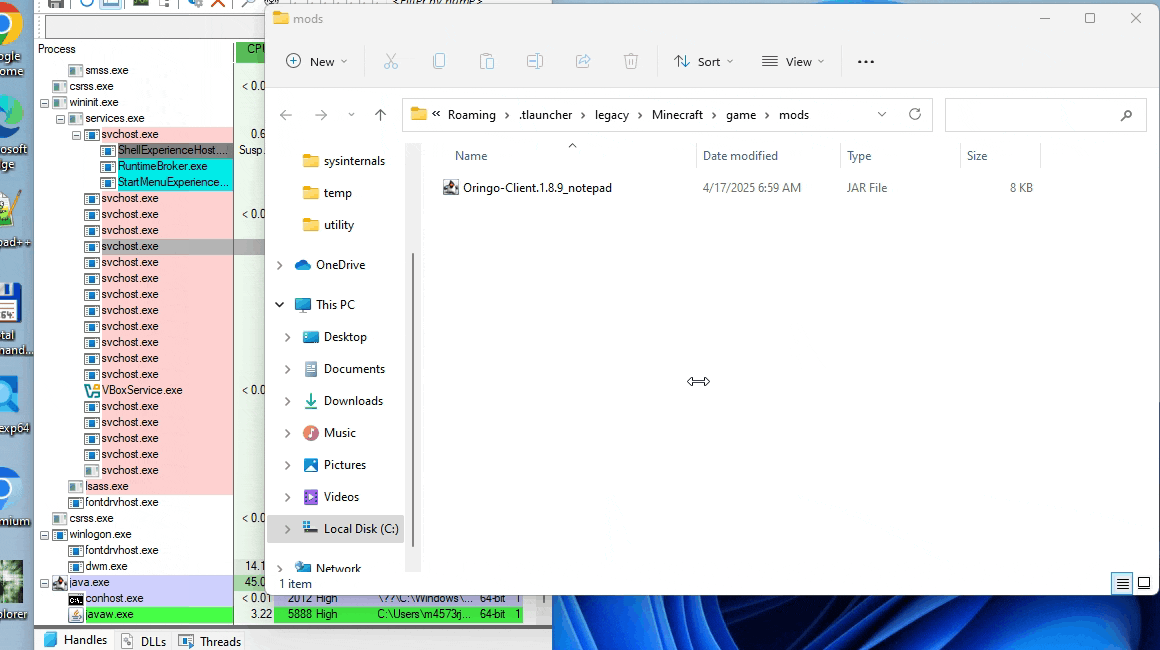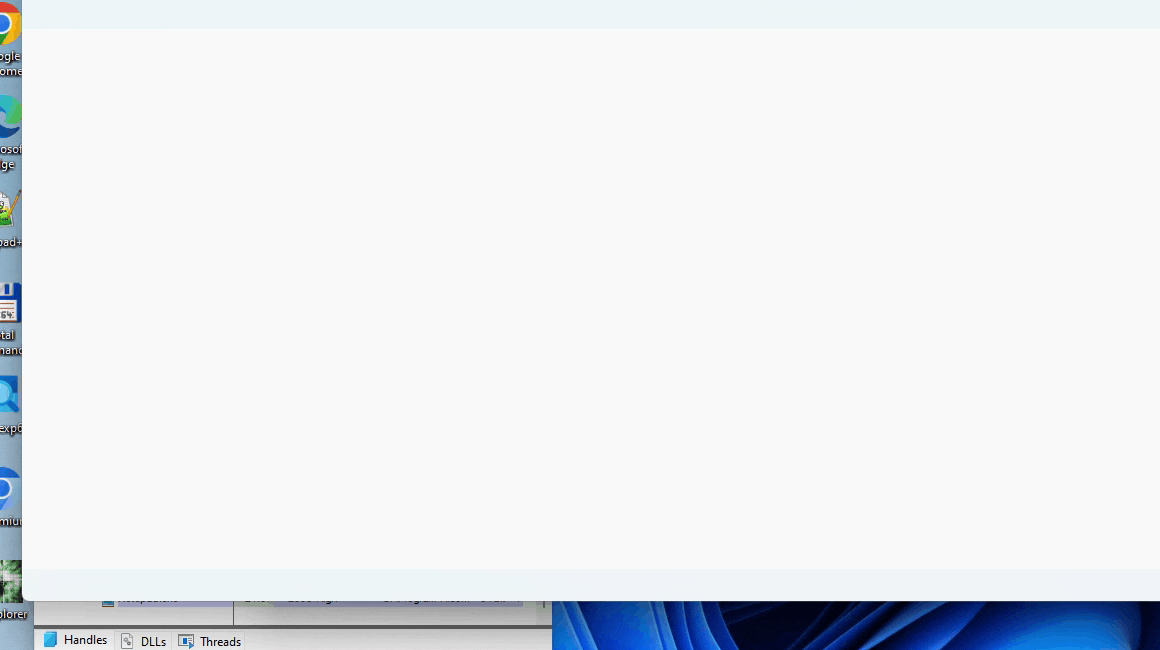

Part III – 2nd Stage Stealer
When the loader successfully passes all the environment checks, it loads the main component, the Stealer. Some samples may be obfuscated with Skidfuscator. The interesting classes and functions of the stealer are shown in the listing below.
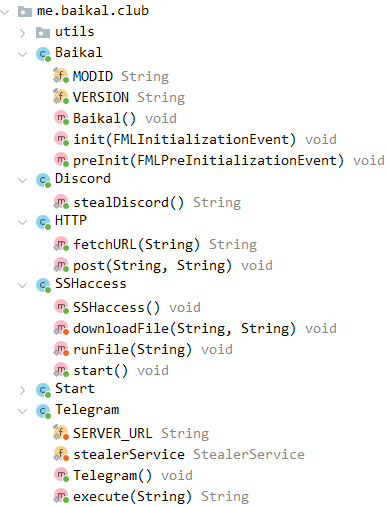
Class Baikal – a class that implements actions performed in the pre-initialization stage
method: init – not implemented
method: preInit – runs start() method from Start class
Class Start
method: start
- download and run .NET stealer
- get external IP from checkip.amazonaws.com
- steal
- Minecraft token
- accounts.json file from Feather client/launcher
- microsoft_accounts.jcon file from Essential client/launcher
- accounts.json file from Lunar client/launcher
- Discord token
- Telegram
- token from pizzaclient
- username
- playerID
- hardcoded type value is set to b0.5, which is likely a version of the stealer
- GET exfiltration URL from Pastebin (hxxps://pastebin[.]com/raw/C9QvUqi3)
- POST the stolen data in JSON format
{
"username": "%s",
"uuid": "%s",
"token": "%s",
"ip": "%s",
"feather": "%s",
"essentials": "%s",
"lunar": "%s",
"discord": "%s",
"type": "%s"
}
Class SSHaccess – class responsible for downloading and executing another file ( .NET stealer), which is analyzed in more detail in section IV.
method: downloadFile
method: runFile
Class Discord – class responsible for stealing Discord tokens. Lists files in %APPDATA%/discord/Local Storage/leveldb, reads the content of files with the extension .ldb, searches for tokens..
method: stealDiscord
Class HTTP – helper class implementing GET and POST requests
method: fetchURL – GET request
method: post – POST request
Class Telegram – class responsible for stealing Telegram data. Finds Telegram’s tdata folder in, zips it, and exfiltrates it.
method: execute
Part IV – 3rd Stage .NET Stealer
The SSHaccess class is responsible for downloading an additional stealer written in .NET and exfiltrating it to a Discord webhook. A webhook is a tool that allows external services or applications to send messages, notifications, or data to a specific Discord channel without needing a bot or user account to be logged in.
[assembly: AssemblyTitle("44 CALIBER")]
[assembly: AssemblyCopyright("FuckTheSystem Copyright © 2021")]
After deobfuscation we can observe that it steals various credentials from browsers (Chromium, Edge, Firefox), files (Desktop, Documents, %USERPROFILE%/Source), Cryptocurrency wallets (Armory, AtomicWallet, BitcoinCore, Bytecoin, DashCore, Electrum, Ethereum, LitecoinCore, Monero, Exodus, Zcash, Jaxx), VPNs (ProtonVPN, OpenVPN, NordVPN), Steam, Discord, FileZilla, Telegram, as well as collects information about the infected machine, such as running processes, external IP, content of clipboard, and takes a screenshot.

Stolen data are zipped, and together with following statistics, commented in Russian, uploaded to Discord webhook.
"\n <@&945424667102031903> fixed file size\n ", Environment.UserName, " ", SystemInfo.Country(), "\n -------------------------\n пассвордс: ", Counting.Passwords.ToString(), "\n -------------------------\n спиздил:", (Counting.Discord > 0) ? "\n - дискорд" : "", (Counting.Wallets > 0) ? "\n - холодки" : "", (Counting.Telegram > 0) ? "\n - тг" : "", (Counting.Steam > 0) ? "\n - стеме" : "", (Counting.NordVPN > 0) ? "\n - нордвпн" : "", (Counting.OpenVPN > 0) ? "\n - открытьвпн" : "", (Counting.ProtonVPN > 0) ? "\n - протонвпн" : ""
Conclusion
A new Java-based malware downloader has remained largely undetected for an extended period. Disguised as Minecraft mods, these malicious Java archives often evade sandbox analysis due to missing dependencies. The Stargazers Ghost Network has been actively distributing this malware, targeting Minecraft players seeking mods to enhance their gameplay. What appeared to be harmless downloads were, in fact, Java-based loaders that deployed two additional stealers, capable of exfiltrating credentials and other sensitive data.
The threat actor behind these campaigns is likely of Russian origin. This case highlights how popular gaming communities can be exploited as effective vectors for malware distribution, emphasizing the importance of caution when downloading third-party content.
Protections
Check Point Threat Emulation and Harmony Endpoint provide comprehensive coverage of attack tactics, filetypes, and operating systems, and protect against the attacks and threats described in this report.
Indicators of Compromise
| Description | SHA256 |
|---|---|
| stage 1 JAR | 05b143fd7061bdd317bd42c373c5352bec351a44fa849ded58236013126d2963 |
| stage 1 JAR | 9ca41431df9445535b96a45529fce9f9a8b7f26c08ac8989a57787462da3342f |
| stage 1 JAR | c5936514e05e8b1327f0df393f4d311afd080e5467062151951e94bbd7519703 |
| stage 1 JAR | 9a678140ce41bdd8c02065908ee85935e8d01e2530069df42856a1d6c902bae1 |
| stage 2 JAR | 4c8a6ad89c4218507e27ad6ef4ddadb6b507020c74691d02b986a252fb5dc612 |
| stage 2 JAR | 51e423e8ab1eb49691d8500983f601989286f0552f444f342245197b74bc6fcf |
| stage 2 JAR | 5d80105913e42efe58f4c325ac9b7c89857cc67e1dcab9d99f865a28ef084b37 |
| stage 2 JAR | 97df45c790994bbe7ac1a2cf83d42791c9d832fa21b99c867f5b329e0cc63f64 |
| stage 2 JAR | 4c944b07832d5c29e7b499d9dd17a3d71f0fd918ab68694d110cbb8523b8af49 |
| stage 2 JAR | 5590eaa4f11a6ed4351bc983e47d9dfd91245b89f3108bfd8b7f86e40d00b9fa |
| stage 2 DL URL | hxxp[://]147[.]45[.]79[.]104/download |
| stage 2 DL URL | hxxp://негры[.]рф/MixinLoader-v2.4[.]jar |
| stage 2 UL URL | hxxp[://]185[.]95[.]159[.]125/upload |
| hosting domain | негры[.]рф |
| stage 3 | 7aefd6442b09e37aa287400825f81b2ff896b9733328814fb7233978b104127f |
| stage 3 | 886a694ee4be77242f501b20d37395e1a8a7a8f734f460cae269eb1309c5b196 |
| stage 3 | a1dc479898f0798e40f63b9c1a7ee4649357abdc757c53d4a81448a5eea9169f |
| stage 3 | a427eeb8eed4585f2d51b62528b8b4920e72002ab62eb6fc19289ebc2fba5660 |
| stage 3 | f08086257c74b1de394bf150ad8aacc99ca5de57b4baa0974bc1b59bb973d355 |
| stage 3 | a1dc479898f0798e40f63b9c1a7ee4649357abdc757c53d4a81448a5eea9169f |
| stage 3 | 886a694ee4be77242f501b20d37395e1a8a7a8f734f460cae269eb1309c5b196 |
| GitHub Repositories | hxxps://github[.]com/A1phaD3v/Oringo-Client |
hxxps://github[.]com/AlphaPigeonDev/Polar-Client hxxps://github[.]com/AlphaPigeonDev/Skyblock-Extras hxxps://github[.]com/P1geonD3v/Funny-Map-Extras hxxps://github[.]com/P1geonD3v/Taunahi-V3 | | | | | | |







